정보
-
업무명 : 대기 환경 자료 처리 및 가시화 : 태양 위치 정보를 이용하여 태양 천정각 (Solar Zenith Angle) 및 태양 방위각 (Solar Azimuth Angle) 가시화
-
작성자 : 이상호
-
작성일 : 2020-03-31
-
설 명 :
-
수정이력 :
내용
[개요]
-
안녕하세요? 기상 연구 및 웹 개발을 담당하고 있는 해솔입니다.
-
대기 환경 정보는 다양한 차원의 관측 자료 및 분석 자료로 구성되어 있기 때문에 이용자가 적절한 분석 및 가시화 기술이 요구됩니다.
-
따라서 오늘 포스팅에서는 태양 위치 정보를 이용하여 태양 천정각 (Solar Zenith Angle) 및 태양 방위각 (Solar Azimuth Angle) 가시화를 소개해 드리고자 합니다.
-
추가로 대기과학 전공자를 위한 IDL를 소개한 링크를 보내드립니다.
[IDL] 아이디엘 대기과학 전공자를 위한 IDL (Interactive Data Language) 소개
정보 업무명 : 대기과학 전공자를 위한 IDL (Interactive Data Language) 소개 작성자 : 이상호 작성일 : 2020-03-23 설 명 : 수정이력 : 내용 [개요] 안녕하세요? 웹 개발 및 연구 개발을 담당하고 있는 해솔입니..
shlee1990.tistory.com
[특징]
-
대기 환경 자료를 이해하기 위해서 자료 처리 및 가시화 기술이 요구되며 이 프로그램은 이러한 목적을 달성하기 위해 고안된 소프트웨어
[기능]
-
시간 및 위/경도에 따른 태양 위치 정보 계산
-
태양 천정각 및 태양 방위각 가시화
[활용 자료]
-
없음
[사용법]
-
입력 자료를 동일 디렉터리에 위치
-
소스 코드를 실행 (idl -e Visualization_Using_Sun_Position)
-
가시화 결과를 확인
[사용 OS]
-
Windows 10
[사용 언어]
-
IDL v8.5
소스 코드
-
해당 작업을 하기 위한 컴파일 및 실행 코드는 IDL로 작성되었으며 가시화를 위한 라이브러리는 Coyote's Guide to IDL Programming를 이용하였습니다.
-
소스 코드는 단계별로 수행하며 상세 설명은 다음과 같습니다.
-
1 단계는 주 프로그램은 작업 경로 설정, 태양 위치 정보를 메모리상에 저장하고 가시화를 위한 초기 설정합니다.
-
2 단계는 plot 매핑에 따라 영상 장면 표출하여 이미지 형식으로 저장합니다. 이 과정에서 포스트 스크립트 (PS) 형식에서 PNG로 변환합니다.
-
[명세]
-
전역 변수 설정
-
cd를 통해 작업 디렉터리 설정
-
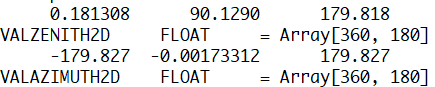
배열 정보 확인 (dim)
-
위도 (lon1D), 경도 (lat1D), 태양 천정각 (valZenith2D), 태양 방위각 (valAzimuth2D)에 대한 배열 설정
-
위도 및 경도는 각각 100 km 간격으로 180 및 360개 격자 구성
-
cd, 'C:\SYSTEM\PROG\IDL\Satellite_Angle'
dim = [360, 180]
lon1D = fltarr(dim[0])
lat1D = fltarr(dim[1])
valZenith2D = fltarr(dim[0], dim[1])
valAzimuth2D = fltarr(dim[0], dim[1])
lon1D = -180.0 + findgen(dim[0])
lat1D = 90.0 - findgen(dim[1])
-
태양 위치 정보 읽기
-
SunPosition 및 시간 (day, hour)과 위/경도 (lat1D, lon1D)를 통해 1차원 태양 천정각 (zenith), 태양 방위각 (azimuth) 계산
-
해당 1차원 결과를 2차원으로 변환
-
for day = 1L, 1 do begin
for hour = 0L, 24 do begin
for iCount = 0L, dim[0] - 1 do begin
SunPosition, day, hour, lat1D, lon1D[iCount], zenith, azimuth
valZenith2D[iCount, *] = zenith[*]
valAzimuth2D[iCount, *] = azimuth[*]
endfor
# 중략
endfor
endfor
-
요약 통계량 확인
-
최소값 (min), 평균값 (mean), 최대값 (max) 계산
-
help를 통해 자료형 및 배열 정보 확인
-
print, min(valZenith2D, /nan), mean(valZenith2D, /nan), max(valZenith2D, /nan)
help, valZenith2D
print, min(valAzimuth2D, /nan), mean(valAzimuth2D, /nan), max(valAzimuth2D, /nan)
help, valAzimuth2D
-
가시화
-
데이터 세트에서 정보는 여전히 숨겨져 있기 때문에 가시화 필요
-
가시화는 일반적인 정적 탐색 데이터 분석에서 웹 브라우저의 동적 대화식 데이터 시각화에 이르기까지 다양함
-
-
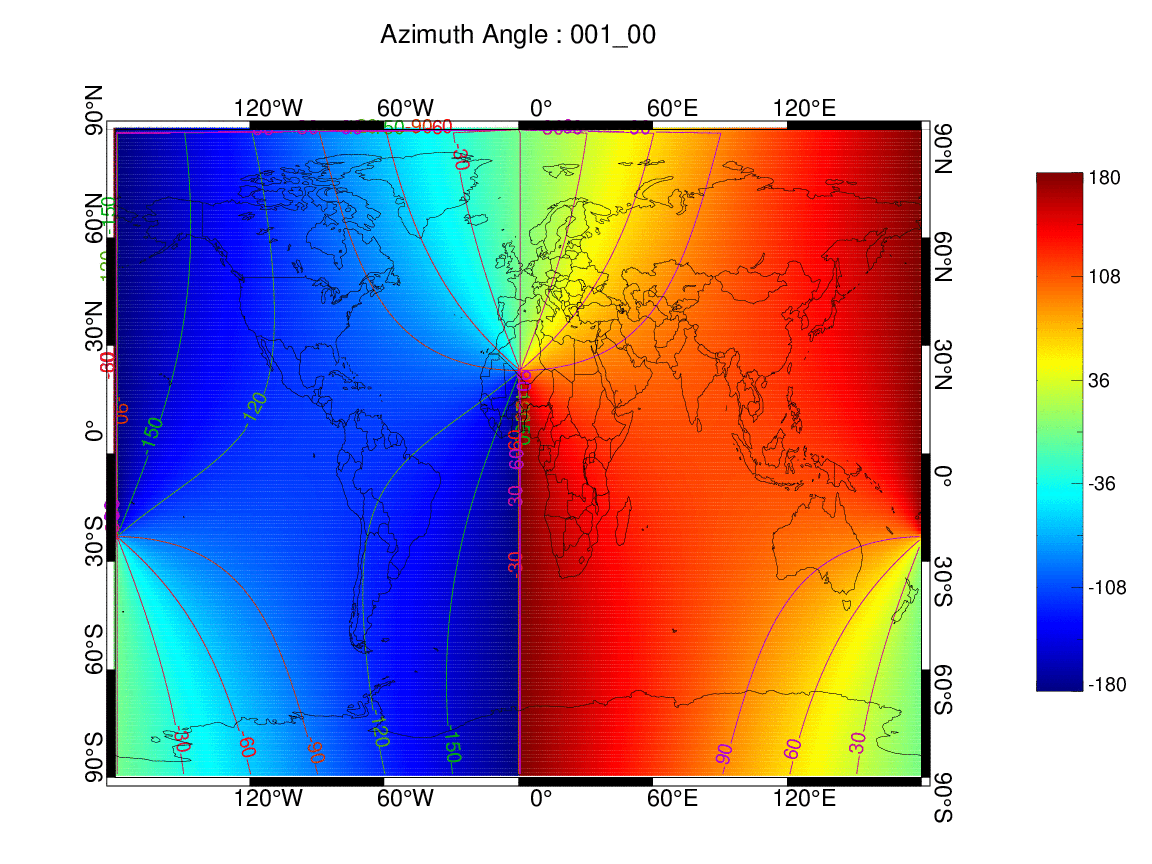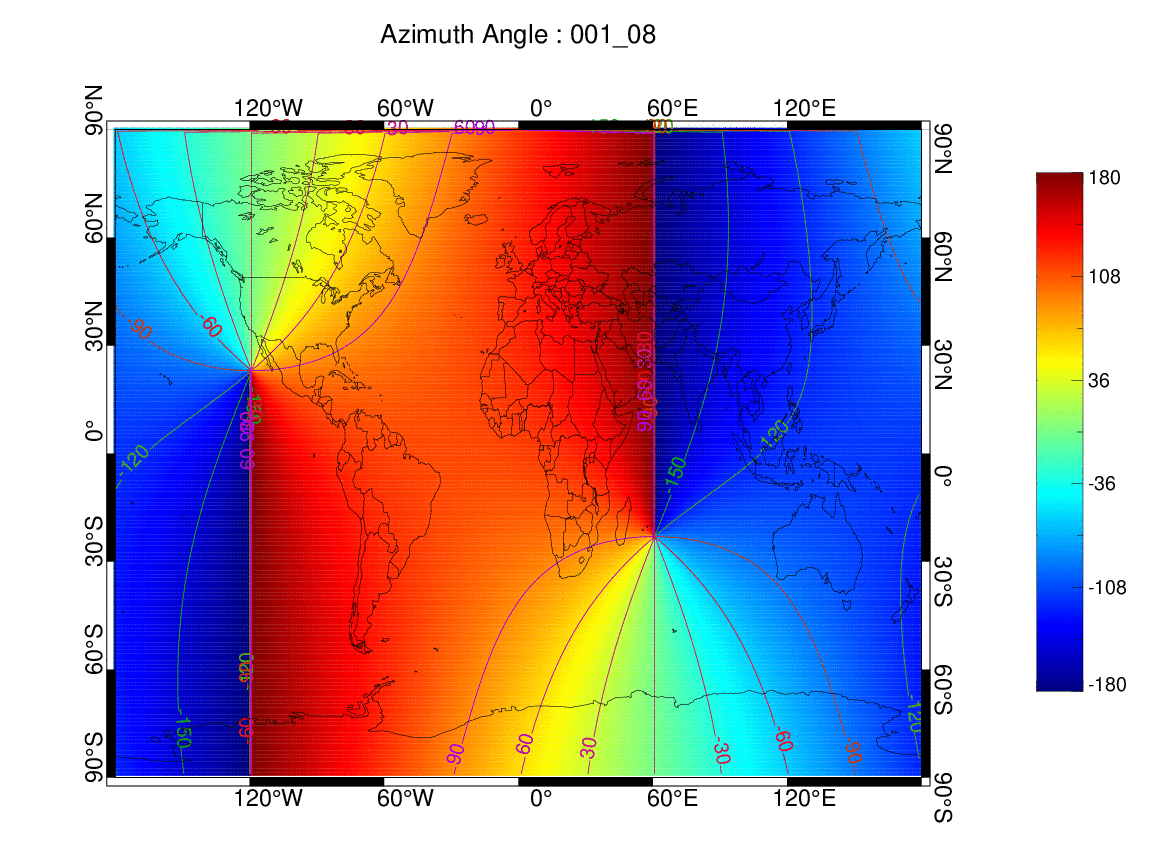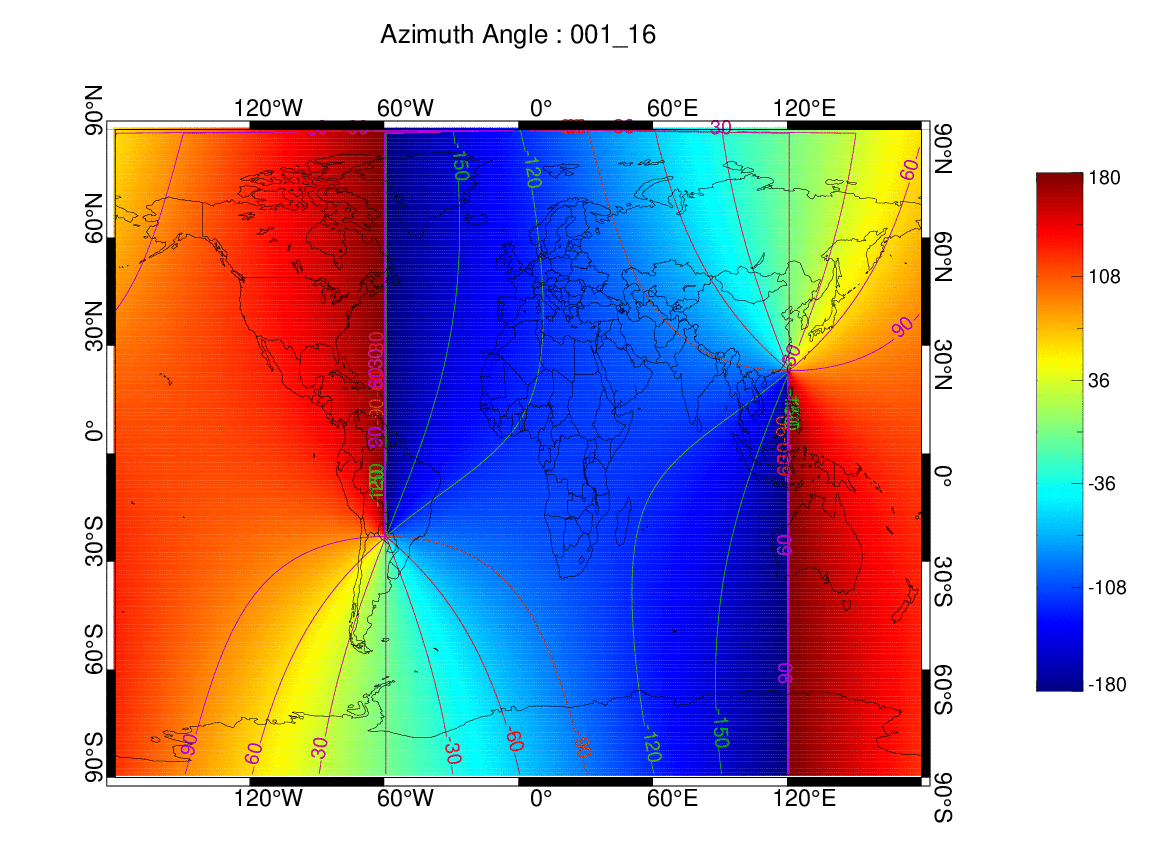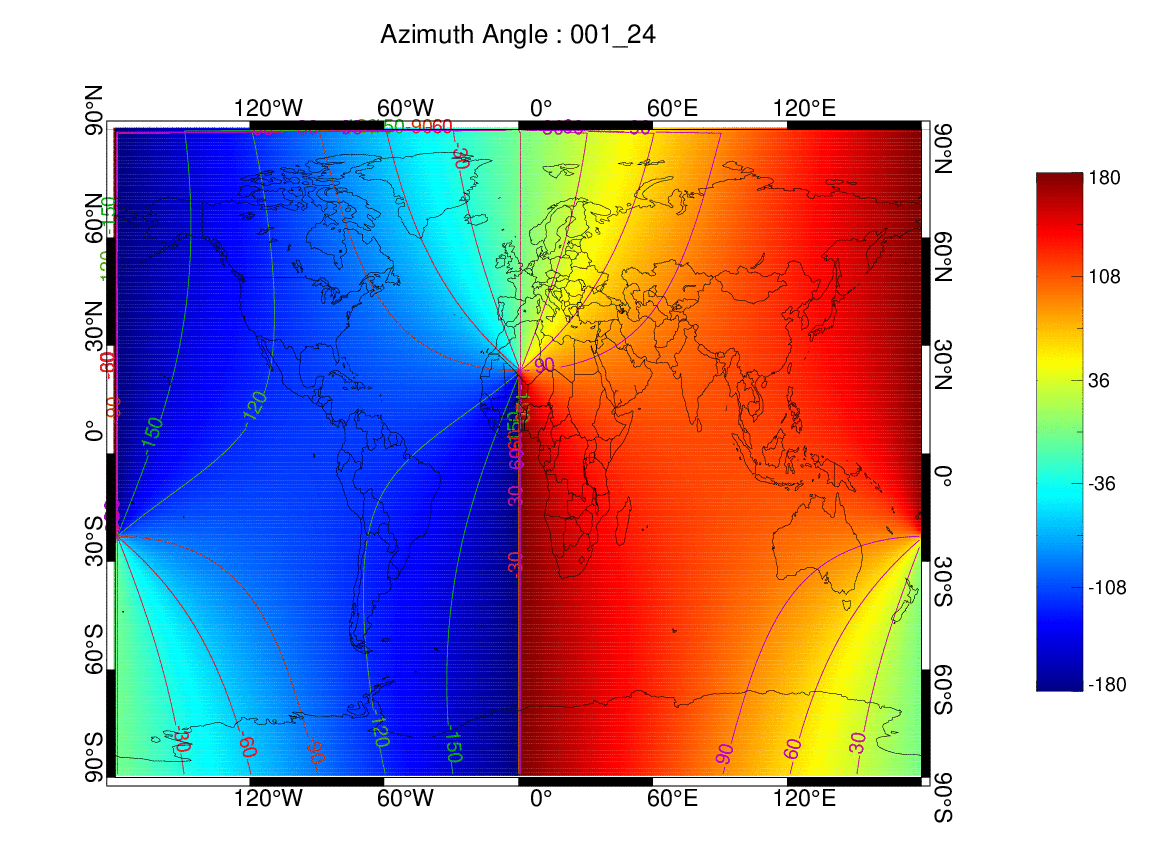
태양 천정각 및 태양 방위각을 위한 설정 및 가시화
-
관심 영역 (ROI)와 중심 위/경도 (cnLon, cnLat) 설정
-
이미지 저장 파일명 (psName) 및 제목명 (mainName)
-
fnMakePsPlot를 통해 이미지 저장
-
cnLat = 0
cnLon = 0
ROI = [-90, 90, -180, 180]
dtDateYmdH = string(day, "_", hour, format='(i3.3, a1, i2.2)')
print, dtDateYmdH
psName = "Img01_" + dtDateYmdH
mainName = "Solar Zenith Angle : " + dtDateYmdH
fnMakePsPlot, lon1D, lat1D, valZenith2D, dim, cnLat, cnLon, ROI, psName, mainName, 0, 180, 30, 33
psName = "Img02_" + dtDateYmdH
mainName = "Azimuth Angle : " + dtDateYmdH
fnMakePsPlot, lon1D, lat1D, valAzimuth2D, dim, cnLat, cnLon, ROI, psName, mainName, -180, 180, 30, 33
-
태양 천정각 (001일 00시)

-
태양 방위각 (001일 00시)

-
동영상 애니메이션 설정
-
반복문 수행한 이후 spawn를 통해 1초마다 동영상 애니메이션 생성
-
com = "convert -loop 0 -delay 100 "+ "./FIG/Img01_*.png" + " " + "./GIF/Img01.gif"
spawn, /hide, com
com = "convert -loop 0 -delay 100 "+ "./FIG/Img02_*.png" + " " + "./GIF/Img02.gif"
spawn, /hide, com
-
태양 천정각 (001일 00-24시)

-
태양 방위각 (001일 00-24시)
-
비디오 동영상
-
태양 천정각 (000-365일 00-24시)
-
태양 방위각 (000-365일 00-24시)
-
사용자 편의성 함수 정의
-
전달 인자
-
1차원 위도 (lon1D), 1차원 경도 (lat1D), 2차원 값 (val2D), 배열 정보 (dim), 중심 위도 (cnLat), 중심 경도 (cnLon), 관심 영역 (ROI), 이미지 저장 파일명 (psName), 제목명 (mainName), 최소값 (zmin), 최대값 (zmax), 등고선 간격 (interval), 컬러 테이블 (color_table)
-
-
기능
-
plot를 통해 위/경도에 따른 값 매핑
-
포스트 스크립트 (PS)를 PNG로 변환
-
-
;====================================================================
; Subroutine : Function Make Postscript to Png Graph
;====================================================================
pro fnMakePsPlot, lon1D, lat1D, val2D, dim, cnLat, cnLon, ROI, psName, mainName, zmin, zmax, interval, color_table
set_plot, "ps"
device, filename = psName + ".ps", decomposed=0, bits=8, /color, xsize=16, ysize = 12, /inches, font_size = 13, /Helvetica
!p.font = 0 & !p.charsize = 2.0 & !p.charthick = 1.6 & !p.multi = [0,1,1] & !p.background = 255
xvert = [0.1, 0.1, -0.1, -0.1 ,0.1]
yvert = [-0.1, 0.1, 0.1, -0.1, -0.1]
usersym, xvert, yvert, /fill
start_color = 0 & end_color = 255 & colorn = end_color - start_color + 1
cgloadct, color_table
latmin = ROI(0) & latmax= ROI(1) & lonmin = ROI(2) & lonmax= ROI(3)
cgMAP_SET, cnLat, cnLon, /CYLINDRICAL $
, limit = [latmin, lonmin, latmax, lonmax] $
, position = [0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.85], /noborder
for i = 0L, dim[0] - 1 do begin
for j = 0L, dim[1] - 1 do begin
nLon = lon1D[i]
nLat = lat1D[j]
nVal = val2D[i, j]
if (lonmin gt nLon or nLon gt lonmax or finite(nLon, /nan) eq 1) then continue
if (latmin gt nLat or nLat gt latmax or finite(nLat, /nan) eq 1) then continue
if (finite(nVal, /nan) eq 1) then continue
plots, nLon, nLat, psym = 8, symsize = 5, color = BYTSCL(nVal, zmin, zmax)
endfor
endfor
cgColorbar, NColors = 255, BOTTOM = 1 $
, Divisions = 5, COLOR = "black" $
, Position = [0.2, 0.90, 0.8, 0.94] $
, Range = [zmin, zmax] $
, CHARSIZE = 1.5,CHARthick = 2 $
, VERTICAL = 1, RIGHT = 1
cgLoadct, 2
contour, val2D, lon1D, lat1D, /overplot, C_THICK = 2 $
, LEVELS = zmin + findgen(10) * interval $
, C_LABELS = zmin + findgen(10) * interval $
, C_CHARSIZE = 1.5, C_CHARTHICK = 2 $
, C_COLORS = BYTSCL(zmin + findgen(10) * interval, zmin, zmax)
cgMAP_CONTINENTS, /coast, /countries, COLOR = "black"
lats = [-90:90:30]
lons = [-180:360:60]
lats_names = strarr(n_elements(lats))
lons_names = strarr(n_elements(lons))
for i = 0L, n_elements(lats) - 1 do begin
if (lats[i] gt 0) then begin
lats_names[i] = textoidl(string(lats[i]) + "\circN")
endif else if (lats[i] eq 0) then begin
lats_names[i] = textoidl(string(lats[i]) + "\circ")
endif else begin
lats_names[i] = textoidl(string(-lats[i]) + "\circS")
endelse
endfor
for i = 0L,n_elements(lons) - 1 do begin
if (lons[i] gt 0) then begin
lons_names[i] = textoidl(string(lons[i]) + "\circE")
endif else if (lons[i] eq 0) then begin
lons_names[i] = textoidl(string(lons[i]) + "\circ")
endif else begin
lons_names[i] = textoidl(string(-lons[i]) + "\circW")
endelse
endfor
cgMap_grid, color = "black", charsize = 1.8, thick = 2.5, lats = lats, latnames = lats_names, lons = lons, lonnames = lons_names $
, linestyle = 1, bthick = 300, /box_axes, /no_grid
cgText, 0.45, 0.95, mainName, /normal, charsize = 2, CHARTHICK = 2, color = "black", alignment = 0.5
device, /close_file
com = "convert -flatten -background white " + psName + ".ps" + " " + "./FIG/" + file_basename(psName, ".ps") + ".png"
spawn, /hide, com
; file_delete, ps_name + ".ps"
return
end
-
태양 위치 정보에 필요한 라이브러리
pro SunPosition,day,time,lat,lon,zenith,azimuth,solfac,sunrise=sunrise, $
sunset=sunset,local=local,latsun=latsun,lonsun=lonsun
;+
; ROUTINE: SunPosition
;
; PURPOSE: Compute solar position information as a function of
; geographic coordinates, date and time.
;
; USEAGE: zensun,day,time,lat,lon,zenith,azimuth,solfac,sunrise,sunset,
; local=local
;
; INPUT:
; day Julian day (positive scalar or vector)
; (spring equinox = 80)
; (summer solstice= 171)
; (fall equinox = 266)
; (winter solstice= 356)
;
; time Universal Time in hours (scalar or vector)
;
; lat geographic latitude of point on earth's surface (degrees)
;
; lon geographic longitude of point on earth's surface (degrees)
;
; OUTPUT:
;
; zenith solar zenith angle (degrees)
;
; azimuth solar azimuth (degrees)
; Azimuth is measured clockwise from due north
;
; solfac Solar flux multiplier. SOLFAC=cosine(ZENITH)/RSUN^2
; where rsun is the current earth-sun distance in
; astronomical units.
;
; NOTE: SOLFAC is negative when the sun is below the horizon
;
;
; KEYWORD INPUT:
;
; local if set, TIME is specified as a local time and SUNRISE
; and SUNSET are output in terms of local time
;
; NOTE: "local time" is defined as UT + local_offset
; where local_offset is fix((lon+sign(lon)*7.5)/15)
; with -180 < lon < 180
;
; Be aware, there are no fancy provisions for
; day-light savings time and other such nonsense.
;
; KEYWORD OUTPUT:
;
; sunrise Time of sunrise (hours)
; sunset Time of sunset (hours)
;
; latsun the latitude of the sub-solar point (fairly constant over day)
; Note that daily_minimum_zenith=abs(latsun-lat)
;
; lonsun the longitude of the sub-solar point
; Note that at 12 noon local time (lon-lonsun)/15. is the
; number of minutes by which the sun leads the clock.
;
;; Often used lat, lon
;
; Santa Barbara: 34.410,-119.727
; SGP Cart Site: 36.605,-97.485
; North Slope: 69.318,-151.015
; Palmer Station: -64.767,-64.067
;
;; EXAMPLE 1: Compute the solar flux at Palmer Station for day 283
;
; time=findgen(1+24*60)/60
; zensun,283,time,-64.767,-64.067,z,a,sf
; solflx=sf*s
; plot,time,solflx
;
; where s is the TOA solar irradiance at normal incidence:
;
; s=1618.8 ; W/m2/micron for AVHRR1 GTR100
; s= 976.9 ; W/m2/micron for AVHRR2 GTR100
; s=1685.1 ; W/m2/micron for 410nm GTR100
; s= 826.0 ; W/m2/micron for 936nm GTR100
; s=1.257e17 ; photons/cm2/s PAR GTR100
; s=1372.9 ; w/m2 total broadband
;
;
;; EXAMPLE 2: Find time of sunrise and sunset for current day
;
; doy=julday()-julday(1,0,1994)
; zensun,doy,12,34.456,-119.813,z,a,s,sunrise=sr,sunset=ss,/local &$
; zensun,doy,[sr,.5*(sr+ss),ss],34.456,-119.813,z,az,/local &$
; print,'sunrise: '+hms(3600*sr)+ ' PST azimuth angle: ',az(0) &$
; print,'sunset: '+hms(3600*ss)+ ' PST azimuth angle: ',az(2) &$
; print,'zenith: '+hms(1800*(ss+sr))+ ' PST zenith angle: ',z(1)
;
; AUTHOR: Paul Ricchiazzi 23oct92
; Earth Space Research Group, UCSB
;
; REVISIONS:
;
; jan94: use spline fit to interpolate on EQT and DEC tables
; jan94: output SUNRISE and SUNSET, allow input/output in terms of local time
; jan97: declare eqtime and decang as floats. previous version
; this caused small offsets in the time of minimum solar zenith
;-
; PROCEDURE:
;
; 1. Calculate the subsolar point latitude and longitude, based on
; DAY and TIME. Since each year is 365.25 days long the exact
; value of the declination angle changes from year to year. For
; precise values consult THE AMERICAN EPHEMERIS AND NAUTICAL
; ALMANAC published yearly by the U.S. govt. printing office. The
; subsolar coordinates used in this code were provided by a
; program written by Jeff Dozier.
;
; 2. Given the subsolar latitude and longitude, spherical geometry is
; used to find the solar zenith, azimuth and flux multiplier.
;
; eqt = equation of time (minutes) ; solar longitude correction = -15*eqt
; dec = declination angle (degrees) = solar latitude
;
; LOWTRAN v7 data (25 points)
; The LOWTRAN solar position data is characterized by only 25 points.
; This should predict the subsolar angles within one degree. For
; increased accuracy add more data points.
;
;nday=[ 1., 9., 21., 32., 44., 60., 91., 121., 141., 152.,$
; 160., 172., 182., 190., 202., 213., 244., 274., 305., 309.,$
; 325., 335., 343., 355., 366.]
;
;eqt=[ -3.23, -6.83,-11.17,-13.57,-14.33,-12.63, -4.2, 2.83, 3.57, 2.45,$
; 1.10, -1.42, -3.52, -4.93, -6.25, -6.28,-0.25, 10.02, 16.35, 16.38,$
; 14.3, 11.27, 8.02, 2.32, -3.23]
;
;dec=[-23.07,-22.22,-20.08,-17.32,-13.62, -7.88, 4.23, 14.83, 20.03, 21.95,$
; 22.87, 23.45, 23.17, 22.47, 20.63, 18.23, 8.58, -2.88,-14.18,-15.45,$
; -19.75,-21.68,-22.75,-23.43,-23.07]
;
; Analemma information from Jeff Dozier
; This data is characterized by 74 points
;
if n_params() eq 0 then begin
xhelp,'zensun'
return
endif
nday=[ 1.0, 6.0, 11.0, 16.0, 21.0, 26.0, 31.0, 36.0, 41.0, 46.0,$
51.0, 56.0, 61.0, 66.0, 71.0, 76.0, 81.0, 86.0, 91.0, 96.0,$
101.0, 106.0, 111.0, 116.0, 121.0, 126.0, 131.0, 136.0, 141.0, 146.0,$
151.0, 156.0, 161.0, 166.0, 171.0, 176.0, 181.0, 186.0, 191.0, 196.0,$
201.0, 206.0, 211.0, 216.0, 221.0, 226.0, 231.0, 236.0, 241.0, 246.0,$
251.0, 256.0, 261.0, 266.0, 271.0, 276.0, 281.0, 286.0, 291.0, 296.0,$
301.0, 306.0, 311.0, 316.0, 321.0, 326.0, 331.0, 336.0, 341.0, 346.0,$
351.0, 356.0, 361.0, 366.0]
eqt=[ -3.23, -5.49, -7.60, -9.48,-11.09,-12.39,-13.34,-13.95,-14.23,-14.19,$
-13.85,-13.22,-12.35,-11.26,-10.01, -8.64, -7.18, -5.67, -4.16, -2.69,$
-1.29, -0.02, 1.10, 2.05, 2.80, 3.33, 3.63, 3.68, 3.49, 3.09,$
2.48, 1.71, 0.79, -0.24, -1.33, -2.41, -3.45, -4.39, -5.20, -5.84,$
-6.28, -6.49, -6.44, -6.15, -5.60, -4.82, -3.81, -2.60, -1.19, 0.36,$
2.03, 3.76, 5.54, 7.31, 9.04, 10.69, 12.20, 13.53, 14.65, 15.52,$
16.12, 16.41, 16.36, 15.95, 15.19, 14.09, 12.67, 10.93, 8.93, 6.70,$
4.32, 1.86, -0.62, -3.23]
dec=[-23.06,-22.57,-21.91,-21.06,-20.05,-18.88,-17.57,-16.13,-14.57,-12.91,$
-11.16, -9.34, -7.46, -5.54, -3.59, -1.62, 0.36, 2.33, 4.28, 6.19,$
8.06, 9.88, 11.62, 13.29, 14.87, 16.34, 17.70, 18.94, 20.04, 21.00,$
21.81, 22.47, 22.95, 23.28, 23.43, 23.40, 23.21, 22.85, 22.32, 21.63,$
20.79, 19.80, 18.67, 17.42, 16.05, 14.57, 13.00, 11.33, 9.60, 7.80,$
5.95, 4.06, 2.13, 0.19, -1.75, -3.69, -5.62, -7.51, -9.36,-11.16,$
-12.88,-14.53,-16.07,-17.50,-18.81,-19.98,-20.99,-21.85,-22.52,-23.02,$
-23.33,-23.44,-23.35,-23.06]
;
; compute the subsolar coordinates
;
tt=((fix(day)+time/24.-1.) mod 365.25) +1. ;; fractional day number
;; with 12am 1jan = 1.
if n_elements(tt) gt 1 then begin
eqtime=tt-tt ;; this used to be day-day, caused
decang=eqtime ;; error in eqtime & decang when a
ii=sort(tt) ;; single integer day was input
eqtime(ii)=spline(nday,eqt,tt(ii))/60.
decang(ii)=spline(nday,dec,tt(ii))
endif else begin
eqtime=spline(nday,eqt,tt)/60.
decang=spline(nday,dec,tt)
endelse
latsun=decang
if keyword_set(local) then begin
lonorm=((lon + 360 + 180 ) mod 360 ) - 180.
tzone=fix((lonorm+7.5)/15)
index = where(lonorm lt 0, cnt)
if (cnt gt 0) then tzone(index) = fix((lonorm(index)-7.5)/15)
ut=(time-tzone+24.) mod 24. ; universal time
noon=tzone+12.-lonorm/15. ; local time of noon
endif else begin
ut=time
noon=12.-lon/15. ; universal time of noon
endelse
lonsun=-15.*(ut-12.+eqtime)
; compute the solar zenith, azimuth and flux multiplier
t0=(90.-lat)*!dtor ; colatitude of point
t1=(90.-latsun)*!dtor ; colatitude of sun
p0=lon*!dtor ; longitude of point
p1=lonsun*!dtor ; longitude of sun
zz=cos(t0)*cos(t1)+sin(t0)*sin(t1)*cos(p1-p0) ; up \
xx=sin(t1)*sin(p1-p0) ; east-west > rotated coor
yy=sin(t0)*cos(t1)-cos(t0)*sin(t1)*cos(p1-p0) ; north-south /
azimuth=atan(xx,yy)/!dtor ; solar azimuth
zenith=acos(zz)/!dtor ; solar zenith
rsun=1.-0.01673*cos(.9856*(tt-2.)*!dtor) ; earth-sun distance in AU
solfac=zz/rsun^2 ; flux multiplier
if n_elements(time) eq 1 then begin
angsun=6.96e10/(1.5e13*rsun) ; solar disk half-angle
;angsun=0.
arg=-(sin(angsun)+cos(t0)*cos(t1))/(sin(t0)*sin(t1))
sunrise = arg - arg
sunset = arg - arg + 24.
index = where(abs(arg) le 1, cnt)
if (cnt gt 0) then begin
dtime=acos(arg(index))/(!dtor*15)
sunrise(index)=noon-dtime-eqtime(index)
sunset(index)=noon+dtime-eqtime(index)
endif
endif
return
end
[전체]
참고 문헌
[논문]
- 없음
[보고서]
- 없음
[URL]
- 없음
문의사항
[기상학/프로그래밍 언어]
- sangho.lee.1990@gmail.com
[해양학/천문학/빅데이터]
- saimang0804@gmail.com
'프로그래밍 언어 > IDL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [IDL] 아이디엘 객체 그래픽 (Object Graphics) 교육 연수 (0) | 2020.05.12 |
|---|---|
| [ENVI] ENVI를 이용한 원격탐사 (Remote Sensing with ENVI) 교육 연수 (0) | 2020.04.03 |
| [IDL] 아이디엘 대기 환경 자료 처리 및 가시화 : Grib 형식인 ECMWF Interim 기상 자료를 이용한 가시화 (0) | 2020.03.31 |
| [IDL] 아이디엘 대기 환경 자료 처리 및 가시화 : HDF5 형식인 천리안위성 1A호 (COMS/MI) 기상 위성 자료를 이용한 에어로졸 광학두께 가시화 (4) | 2020.03.31 |
| [IDL] 아이디엘 대기 환경 자료 처리 및 가시화 : HDF 형식인 전지구 오존량 자료를 이용한 가시화 (0) | 2020.03.31 |

